European nuclear power plant construction: success stories and benefits

France and Germany have been at the forefront of nuclear power plant construction in Europe, contributing to significant advancements and benefits in the energy sector, Kazinform News Agency correspondent reports.
French company Electricité de France (EDF) has spearheaded numerous projects both domestically and internationally, with notable plants in Flamanville, Paluel, and Gravelines. French expertise extends beyond its borders to the United Kingdom, with EDF playing a pivotal role in the Hinkley Point C project, and in Finland's Olkiluoto plant.

Germany, despite its recent decision to phase out nuclear power by 2022, has a history of substantial contributions to nuclear projects. Key plants like Emsland and Gundremmingen have been instrumental in the country's energy landscape. German engineering has also supported international nuclear initiatives.

Other European nations join the nuclear movement
Several other European countries have embraced nuclear power. The United Kingdom continues to develop Hinkley Point C, while Finland benefits from the Olkiluoto plant. The Czech Republic's Temelín, Hungary's Paks II, Slovakia's Mochovce, and Belarus's Astravets (with Russian collaboration) highlight the widespread adoption of nuclear energy across Europe.

Cutting-edge nuclear technologies
European nuclear projects employ various advanced technologies to enhance efficiency and safety. France’s Pressurised Water Reactors (PWR), such as the European Pressurised Reactor (EPR) used in Hinkley Point C and Flamanville, are renowned for their reliability. Boiling Water Reactors (BWR), prevalent in Sweden and Finland, offer another robust solution.
The Water-Water Energetic Reactor (VVER), a Russian technology, is used in Hungary and Slovakia, known for its enhanced safety features. The UK’s unique Advanced Gas-cooled Reactors (AGR) continue to provide energy despite no new constructions. Emerging Small Modular Reactors (SMR) are gaining interest for their flexibility and safety, with the UK leading development efforts.
Positive impacts and advantages
Nuclear power ensures a stable and reliable energy supply, as seen in France, where approximately 70% of electricity is generated from nuclear power, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and shielding the country from energy price volatility.
Additionally, nuclear plants emit significantly lower greenhouse gases compared to fossil fuel-based power plants, helping countries like Finland achieve climate goals and reduce their carbon footprints.
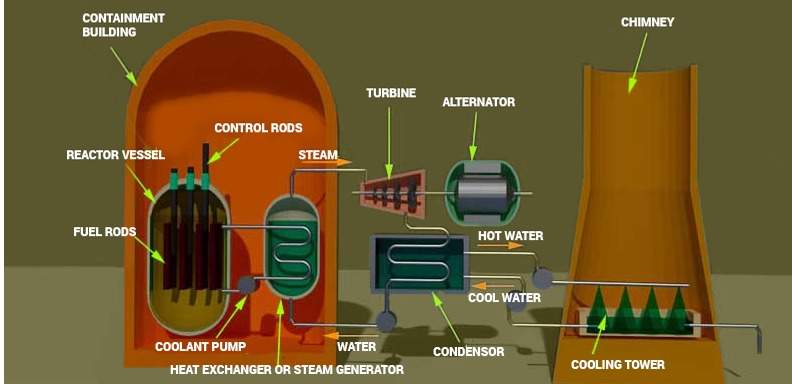
The construction and operation of nuclear power plants also create jobs and stimulate local economies. For example, Hinkley Point C in the UK has generated thousands of jobs and boosted regional economic activity.
Furthermore, investing in nuclear power positions countries as leaders in technological innovation, exemplified by France's development of the European Pressurised Reactor (EPR).
Nuclear energy provides predictable and stable energy costs, which is crucial for economic planning. Countries such as Hungary and the Czech Republic benefit from the price stability offered by nuclear power.
Modern nuclear reactors have a lifespan exceeding 60 years, ensuring long-term energy solutions and sustainable benefits for countries investing in nuclear technology.
The experience of European countries in nuclear power plant construction underscores the immense benefits of nuclear energy. From enhanced energy security and environmental advantages to economic growth and technological leadership, nuclear power remains a valuable asset. As new technologies evolve and safety measures improve, the role of nuclear energy in Europe’s future is poised to remain significant.

